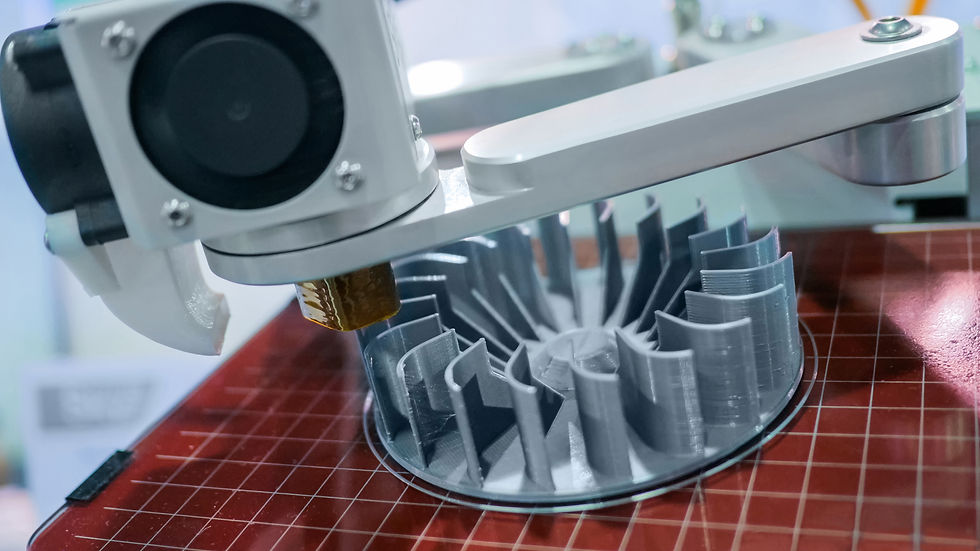
Additive Manufacturing, Subtractive Waste: How 3D Printing is Changing Sustainability
- Dylan Brubacher
- Apr 3
- 3 min read
As the world shifts towards more sustainable practices, industries are looking for ways to reduce waste, lower carbon emissions, and make better use of resources. 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, has emerged as a revolutionary solution that is inherently more environmentally friendly than traditional manufacturing methods. By minimizing material waste, reducing energy consumption, and enabling localized production, 3D printing is paving the way for a greener future.
Reducing Material Waste
Traditional manufacturing methods, such as CNC machining, injection molding, and casting, often involve subtractive processes where large amounts of material are cut away and discarded. In contrast, 3D printing is an additive process, meaning material is deposited layer by layer, using only what is needed to create the final product. This results in:
Significantly less material waste, as unused filament or resin can often be recycled or reused.
More efficient use of raw materials, reducing the need for excess inventory and overproduction.
Customization without additional waste, allowing for unique designs without requiring new molds or tooling.
Lower Energy Consumption
While traditional manufacturing requires energy-intensive processes such as forging, milling, and transportation of materials, 3D printing operates on a much more efficient energy model. Key energy-saving benefits include:
On-demand production, reducing the need for mass production and large storage facilities.
Less reliance on energy-intensive machinery, as 3D printers often require lower operating temperatures compared to traditional manufacturing techniques.
Direct manufacturing from digital files, eliminating the need for multiple machining steps and tooling changes.
Eco-Friendly Materials and Recycling
The materials used in 3D printing are becoming increasingly sustainable, with innovations focused on biodegradable and recycled materials. Some key developments include:
PLA (Polylactic Acid) – A popular biodegradable plastic derived from cornstarch or sugarcane, making it an excellent alternative to petroleum-based plastics.
Recycled Filaments – Many companies now produce filaments made from recycled plastic bottles, reducing landfill waste and repurposing materials.
Bio-based Resins – New formulations of plant-based resins are being developed to reduce reliance on synthetic, petroleum-derived resins.
Metal and Composite Recycling – Some 3D printing processes, such as metal powder bed fusion, allow for unused metal powder to be reclaimed and reused in future prints.
Localized and On-Demand Manufacturing
One of the most impactful environmental benefits of 3D printing is the ability to produce parts locally, reducing the need for global shipping and long supply chains. This leads to:
Lower carbon footprint, as products can be printed near the point of use instead of being transported long distances.
Decreased packaging waste, since parts can be printed as needed rather than stored and shipped in bulk.
Faster response times, allowing for more sustainable just-in-time production models that eliminate excess stock and reduce waste.
Extended Product Lifespan and Repairability
3D printing also plays a crucial role in sustainability by enabling easy repairs and extending the lifespan of products. Instead of discarding broken items, consumers and businesses can:
Print replacement parts on demand, reducing electronic and mechanical waste.
Modify and improve existing products, adapting designs instead of purchasing entirely new items.
Use open-source and shared digital designs, minimizing the need for proprietary components that become obsolete.
Sustainable Prototyping and Innovation
For businesses and startups, prototyping is a necessary step in product development, but traditional prototyping methods often lead to excessive waste. With 3D printing:
Rapid prototyping minimizes waste, as only necessary prototypes are printed, and digital modifications are made without material loss.
Cost-effective and sustainable testing, reducing the need for large-scale, resource-intensive prototype manufacturing.
Efficient design iteration, allowing for multiple revisions without the need for excessive material use.
Lower Consumption, Increase Sustainabilty
Compared to traditional manufacturing, 3D printing offers a clear path toward more sustainable production. By reducing material waste, lowering energy consumption, enabling local manufacturing, and promoting recyclable and biodegradable materials, 3D printing is setting the stage for a greener, more efficient future. As technology advances and materials continue to improve, the environmental benefits of 3D printing will only become more significant, making it a vital tool in the transition to sustainable manufacturing practices.
.png)